Whois è un tool per il protocollo RFC 3912, che interroga i server online per ottenere informazioni come dettagli di contatto per domini e assegnazioni di indirizzi IP.
Il tool contiene anche mkpasswd, un'interfaccia ricca di funzionalità per la funzione di cifratura delle password crypt.
Whois è già installato in moltissimi sistemi operativi di default ma vediamo il comando di installazione.

Installazione:
Comandi base:
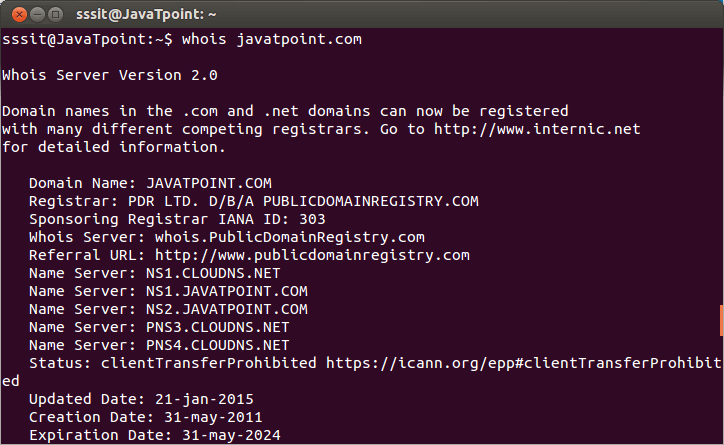
Comando per interrogare un server web da url del sito:
whois ethicalhacking.freeflarum.com
Il tool vi darà in seguito molte informazioni ad esempio ID del dominio, stato del dominio, nome del server ecc...
Molto simile il comando per interrogare un IP:
whois x.x.x.x
Funzioni complete di mkpasswd:
mkpasswd -h
Usage: mkpasswd [OPTIONS]... [PASSWORD [SALT]]
Crypts the PASSWORD using crypt(3).
-m, --method=TYPE select method TYPE
-5 like --method=md5crypt
-S, --salt=SALT use the specified SALT
-R, --rounds=NUMBER use the specified NUMBER of rounds
-P, --password-fd=NUM read the password from file descriptor NUM
instead of /dev/tty
-s, --stdin like --password-fd=0
-h, --help display this help and exit
-V, --version output version information and exit
Funzioni complete di Whois:
whois --help
Usage: whois [OPTION]... OBJECT...
-h HOST, --host HOST connect to server HOST
-p PORT, --port PORT connect to PORT
-I query whois.iana.org and follow its referral
-H hide legal disclaimers
--verbose explain what is being done
--no-recursion disable recursion from registry to registrar servers
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
These flags are supported by whois.ripe.net and some RIPE-like servers:
-l find the one level less specific match
-L find all levels less specific matches
-m find all one level more specific matches
-M find all levels of more specific matches
-c find the smallest match containing a mnt-irt attribute
-x exact match
-b return brief IP address ranges with abuse contact
-B turn off object filtering (show email addresses)
-G turn off grouping of associated objects
-d return DNS reverse delegation objects too
-i ATTR[,ATTR]... do an inverse look-up for specified ATTRibutes
-T TYPE[,TYPE]... only look for objects of TYPE
-K only primary keys are returned
-r turn off recursive look-ups for contact information
-R force to show local copy of the domain object even
if it contains referral
-a also search all the mirrored databases
-s SOURCE[,SOURCE]... search the database mirrored from SOURCE
-g SOURCE:FIRST-LAST find updates from SOURCE from serial FIRST to LAST
-t TYPE request template for object of TYPE
-v TYPE request verbose template for object of TYPE
-q [version|sources|types] query specified server info
In conclusione le funzioni del tool whois sono disponibili da moltissimi siti web dedicati a questo ma ovviamente averlo da terminale può essere più comodo!
WHOIS è un tool molto utilizzato per reperire database contenenti utenti registrati, come un nome di dominio o indirizzi IP, ma è utilizzato anche per trovare molte altre informazioni.